epithalon
$475.00 – $2,375.00
epithalon (Epitalon) is a synthetic derivative of Epithalamin and a potential modulator of telomerase, the enzyme that maintains and protects the telomere caps at the ends of chromosomes (strands of DNA). Research suggests that Epithalon induces telomere elongation and may fight off the effects of aging as a result.
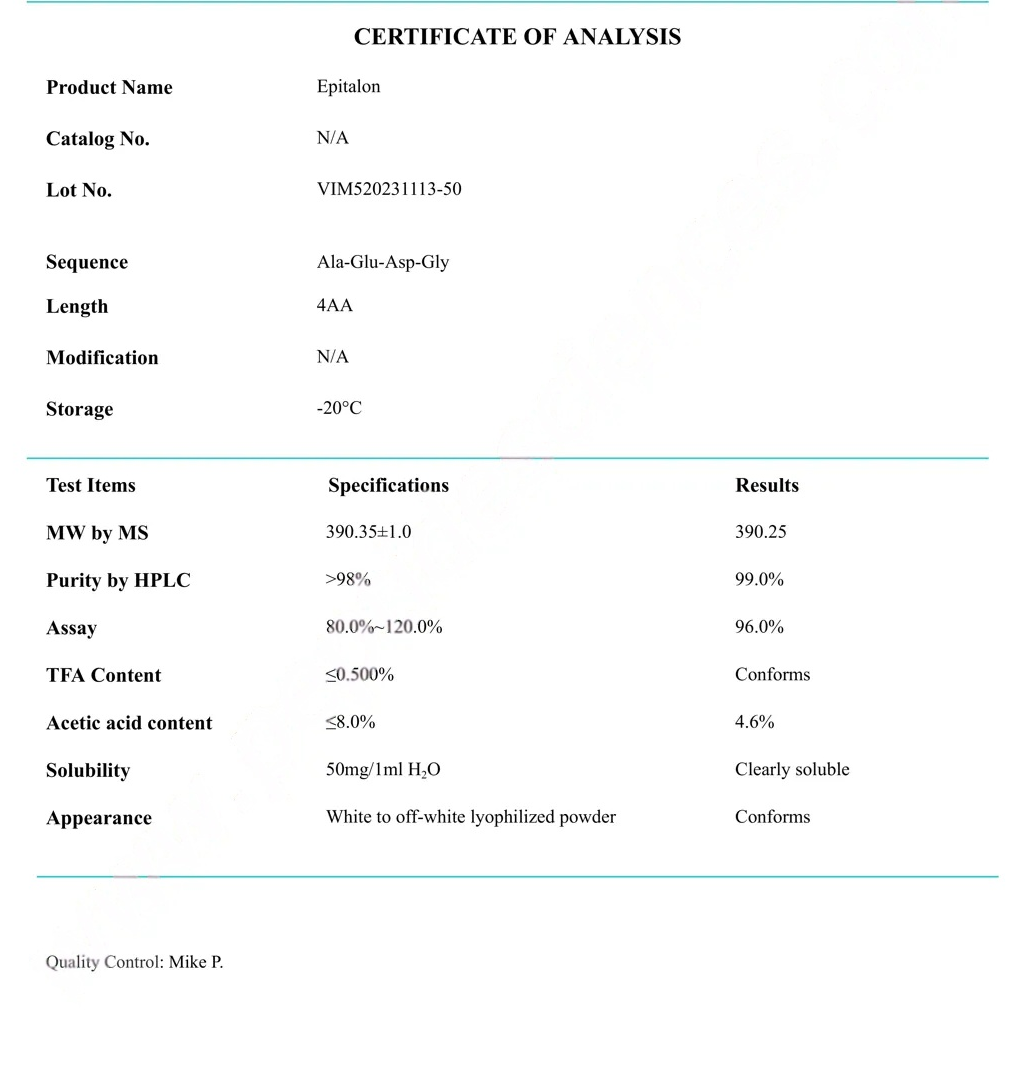
COA epithalon (Epitalon) Certificate
epithalonalso known as Epitalon, Epithalone or Epithalamin) is a short synthetic peptide known to activate the telomerase enzyme and stimulate melatonin release. First developed in Russia in the 1980s, epithalon has been shown to delay age-related changes in reproductive and immune systems and increase the life span of mice and rats. Though it is primarily of interest in anti-aging research, epithalon has shown significant effects in certain types of cancer, infectious disease, and in DNA regulation.
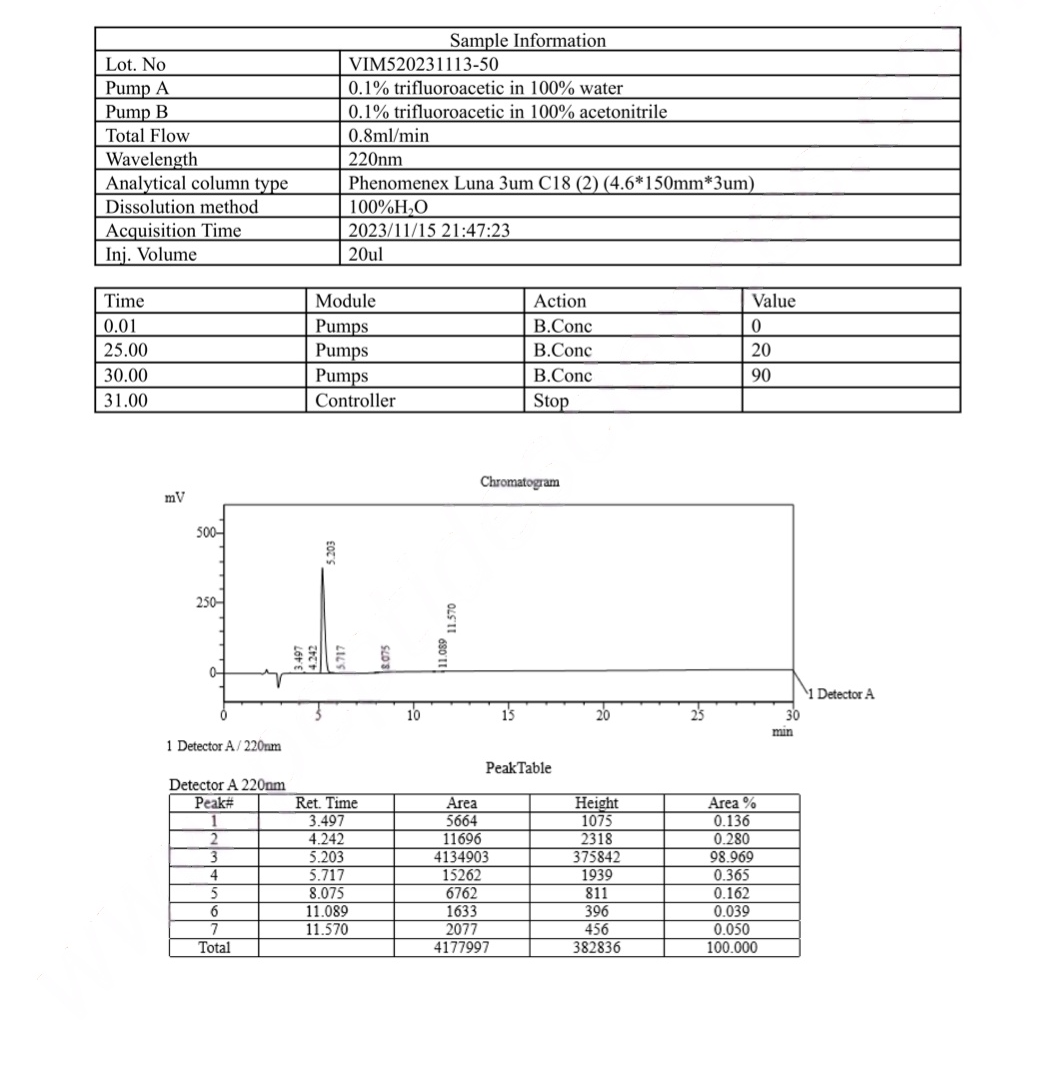
HPLC epithalon (Epitalon) Certificate
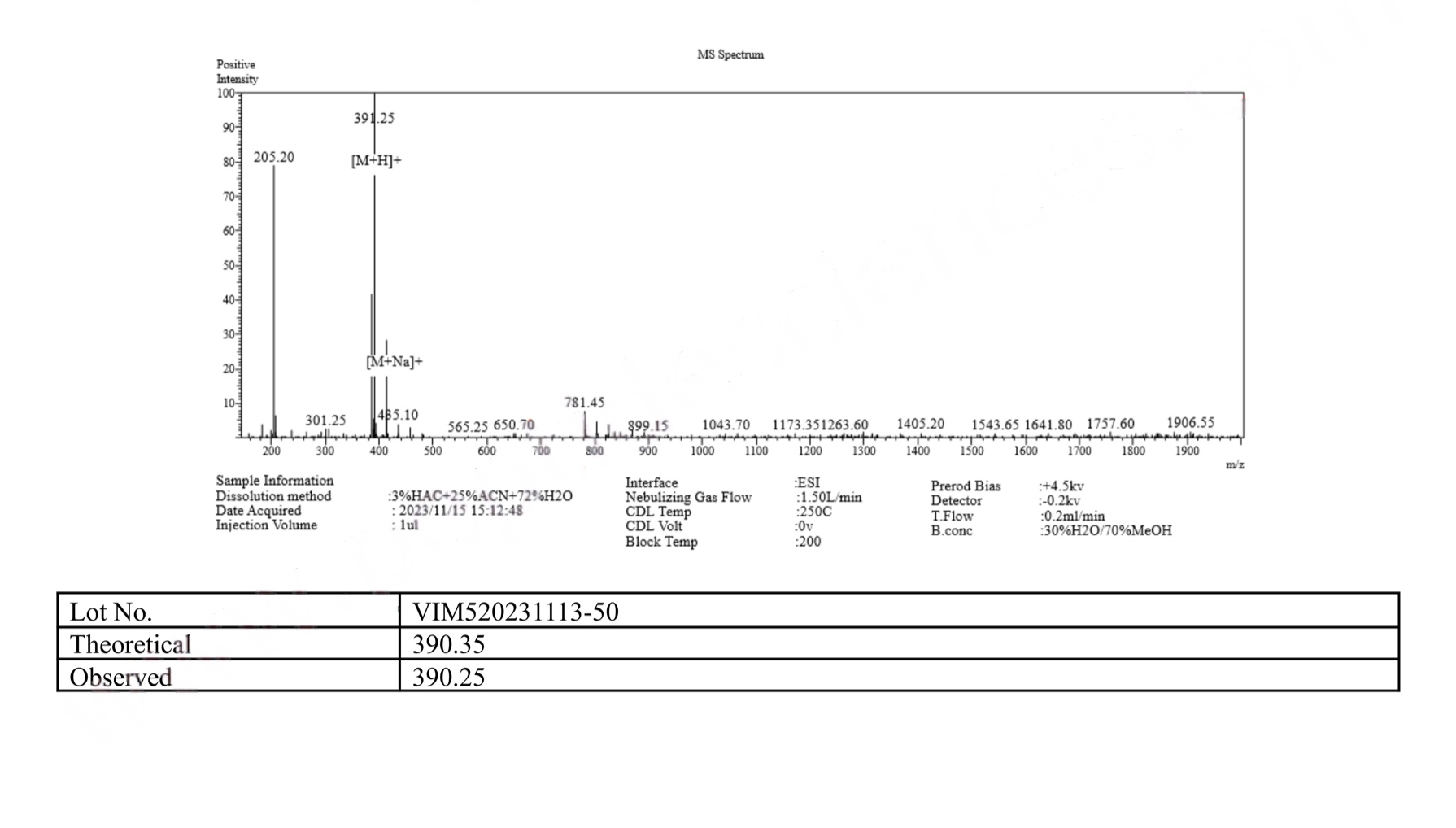
MS Epithalon (Epitalon) Certificate
epithalon Research
1. The Role of Telomerase in the Anti-Aging Effects of Epithalon
Early research using insects and rodents revealed that epithalon can prolong life substantially. In normal, healthy fruit flies and rats, epithalon decreases mortality by 52%. In mice prone to both heart disease and cancer, epithalon prolongs life by as much as 27% compared to controls[1]. At least part of the answer to how epithalon achieves these profound effects is via its elimination of free radicals (charged molecules that do damage to healthy tissue).
Anti-oxidant activity is not the only reason that epithalon extends life, however. There is good evidence from in vitro experiments on human somatic cells to show that epithalon activates an enzyme called telomerase[2]. Telomerase protects telomeres, the ends of chromosomes that are critical to ensuring the health of DNA. Epithalon’s activation of telomerase leads directly to a decrease in how many errors a strand of DNA contains, supporting the notion that epithalon protects DNA from damage [3], [4]. In short, epithalon protects DNA from accumulating errors over time, a process that eventually leads to cell dysfunction, aging, and even cancer in some cases.
2. Epithalon and DNA Activation
Neither its impact on free radicals nor its effects on telomeres seem sufficient to explain the profound effects that epithalon has on longevity. Indeed, scientists are working hard to understand how this short peptide achieves the effects that it does so that the mechanisms can be explored in depth. As it turns out, at least part of the answer may come from the fact that epithalon changes the expression of certain genes.
Research in cell cultures shows that epithalon interacts directly with DNA to turn on and enhance the expression of certain genes. Epithalon interacts with the promoter regions of genes for CD5, IL-2, MMP2, and Tram1[5]. CD5 and IL-2 both affect the function of the immune system while MMP2 plays a critical role in the maintenance of extracellular matrix in skin, tendons, and other connective tissue. These findings suggest that epithalon may impact the function of the immune system and the ability of the body to heal itself following not only injury, but following typical day-to-day stress as well.
It is not surprising that epithalon impacts the immune system. Research in rats indicates that epithalon boost the expression of interferon gamma in aging lymphocytes[]. Interferon gamma is a critical signaling molecule in the immune system. It is important for fighting off viral infections through the activation of macrophages, natural killer cells, and T cells.
3. Epithalon and Skin Health
As stated above, epithalon has a positive effect on the gene that regulates MMP2. MMP2 is a protein found in connective tissue like skin. Research in rodents indicates that not only does epithalon activate this gene, it activates fibroblasts, the cells that produce and maintain MMP2 as well as other components of the extracellular matrix like collagen and elastin. Mice exposed to epithalon show an increase in fibroblast activation of 30-45%[7]. By activating fibroblasts, epithalon can help to boost rates of healing and offset the natural decline in skin structure and integrity that occurs with aging.
Further evidence for epithalon’s benefit in skin comes from the fact that it decreases caspase-3 activity. Caspase-3 is an enzyme in the apoptosis or programmed cell death pathway. By decreasing caspase-3 activity, epithalon helps to protect fibroblasts and other skin cells, keeping them alive and healthy for longer periods of time[8].
4. Epithalon and Tumor Growth
Daily administration of epithalon to rats with cancer has been found to decrease tumor growth[]. Not only does the peptide reduce tumor growth, it prevents the metastasis or spread of these tumors to distant tissues as well [10], [11]. Epithalon is currently being investigated as a potential treatment for Her-2/neu positive breast cancers and is of interest in preventing the development of certain types of leukemia as well as testicular cancer
5. Epithalon and Melatonin Secretion
Melatonin, which is linked to sleep and aging, is produced by the pineal gland. Research in rats shows that epithalon and similar peptides affect both the synthesis and release of melatonin by affecting the expression of two proteins (arylalkylamine-N-acetyltransferase (AANAT) and pCREB transcription protein) [15]. Both of these genes play an important role in melatonin production and in the circadian (day/night) control of melatonin release. Research in monkeys indicates that epithalon restores melatonin secretion to normal [16].
6. Epithalon and Eyesight
A trial in rats suffering from retinitis pigmentosa found that epithalon improves outcomes in 90% of patients [17]. It appears that the peptide helps to preserver normal structure of the eye while boosting the bioelectric function of the retina necessary for vision.
Epithalon exhibits minimal side effects, low oral and excellent subcutaneous bioavailability in mice. Per kg dosage in mice does not scale to humans. Epithalon for sale at Peptide Sciences is limited to educational and scientific research only, not for human consumption. Only buy Epithalon if you are a licensed researcher.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is epithalon (Epitalon)?
Epithalon, also known as Epitalon or AEDG, is a synthetic tetrapeptide composed of the amino acids alanine, glutamic acid, aspartic acid, and glycine. It was developed to mimic the natural peptide epithalamin, produced by the pineal gland, and is primarily utilized in scientific research focusing on aging, cellular health, and longevity.
2. What are the primary research applications of epithalon?
Epithalon has been extensively studied for its potential effects on:
-
Telomerase Activation: Stimulating telomerase activity, which may lead to telomere elongation and delayed cellular aging.
-
Melatonin Regulation: Normalizing melatonin production in the pineal gland, potentially improving circadian rhythms and sleep patterns.
-
Antioxidant Properties: Reducing oxidative stress and normalizing T-cell function, contributing to improved immune response.
-
Gene Expression Modulation: Influencing gene expression related to neuronal differentiation and protein synthesis in human stem cells.
3. Is epithalon approved for human consumption?
No, Epithalon is intended strictly for laboratory research use only. It is not approved for human consumption, medical, or veterinary use.
4. How should epithalon be stored?
-
Lyophilized (Powder) Form:
-
Short-term Storage: Stable at room temperature for several days to weeks.
-
Long-term Storage: Store at -20°C or colder to maintain stability.
-
-
Reconstituted (Solution) Form:
-
Short-term Storage: Stable for 3 or more weeks at +4°C.
-
Long-term Storage: Store at -20°C for 3-4 months.
-
-
General Guidelines:
-
Protect from intense light.
-
Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles to prevent degradation.
-
5. What is the recommended method for reconstituting epithalon?
Epithalon can be reconstituted using sterile water or bacteriostatic water. It is advisable to aliquot the solution to avoid multiple freeze-thaw cycles. The stability of the solution depends on the solvent used, pH (optimal pH 5-7), and the amino acid sequence.
6. Are there any known side effects associated with epithalon?
In research settings, some uncommon and typically mild side effects have been reported, including:
-
Fatigue: Temporary feelings of tiredness.
-
Headaches: Mild to moderate headaches. These side effects usually resolve without intervention.
7. What are the available vial sizes for epithalon?
Epithalon is available in various quantities to accommodate different research needs:
-
10mg Vial: Suitable for preliminary studies and small-scale experiments.
-
25mg Vial: Ideal for extended research projects requiring moderate quantities.
-
50mg Vial: Best for large-scale studies and repeated experimentation.
Vendor: PeptideNationUSA
| Quantity | 10mg * 10 vials, 25mg * 10 vials, 50mg * 10 vials |
|---|
Be the first to review “epithalon” Cancel reply
Related products
Bioregulators
Bioregulators
Bioregulators
Bioregulators
Bioregulators
Bioregulators
Bioregulators
Bioregulators











Reviews
There are no reviews yet.